Have you ever wondered about the connection between the sun and your overall well-being? The sun plays a crucial role in our lives, providing us with warmth, light, and energy. But its impact on our health goes far beyond that. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating relationship between the sun and our bodies, exploring the ways in which sun exposure affects our physical and mental health. From the production of vital nutrients like vitamin D to its influence on serotonin levels and sleep patterns, the sun has a profound effect on our bodies and minds. So, let’s uncover the secrets of the sun and discover how it can contribute to a healthier, happier you.
1. How Sun Exposure Affects Your Health
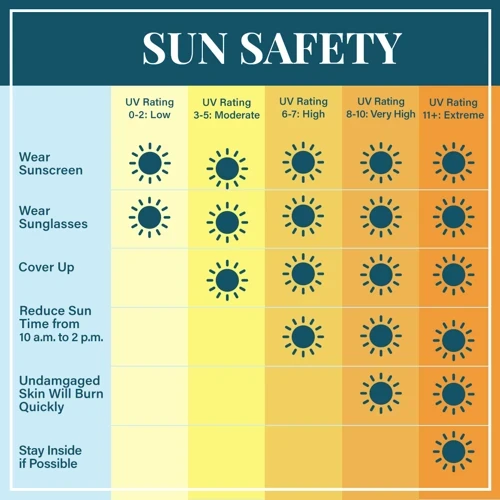
Sun exposure has a profound impact on our health, affecting various aspects of our well-being. One of the key roles the sun plays is in the production of Vitamin D. When our skin is exposed to sunlight, it triggers a process that synthesizes Vitamin D, an essential nutrient for our bodies. Vitamin D is not only crucial for the absorption of calcium and maintaining strong bones, but it also supports our immune system and promotes overall good health. Another aspect to consider is the relationship between sun exposure and skin health. While spending time in the sun can have positive effects, such as a healthy complexion and increased production of melanin for sun protection, it’s important to be mindful of the risk of sunburns. Excessive exposure to the sun’s ultraviolet (UV) radiation can damage our skin cells and increase the risk of skin cancer. It’s crucial to find a balance between reaping the benefits of sun exposure and protecting our skin from harm.
1.1 Sun’s Role in Vitamin D Production
The sun plays a crucial role in the production of Vitamin D in our bodies. When our skin is exposed to sunlight, specifically the ultraviolet B (UVB) rays, a remarkable process is set in motion. In this process, a cholesterol-like compound present in our skin called 7-dehydrocholesterol is converted into vitamin D3. The uvb rays transform the compound, and eventually, when it reaches the liver and kidneys, it’s converted into its active form, calcitriol, which has multiple important functions in our bodies.
Vitamin D is known as the “sunshine vitamin” because sunlight is one of the primary sources of its production. While it can also be obtained through certain foods and supplements, the sun’s rays are particularly efficient in promoting the synthesis of this essential nutrient. This is why spending time outdoors and exposing our skin to sunlight is crucial for maintaining adequate levels of vitamin D.
Vitamin D plays a key role in various bodily functions, including calcium absorption, bone health, and immune function. It helps regulate the levels of calcium and phosphorus in our bodies, which are essential for strong and healthy bones. Vitamin D is involved in the modulation of our immune system, assisting in the defense against infections and supporting overall immune function.
It’s worth noting that certain factors can influence the production of vitamin D in our bodies. These factors include the geographical location, time of day, season, skin pigmentation, and the use of sunscreen. Individuals living in higher latitudes or areas with limited sunlight may have difficulty producing adequate amounts of vitamin D naturally. Similarly, people with darker skin pigmentation may require longer sun exposure to produce the same amount of vitamin D as those with lighter skin.
To ensure optimal vitamin D production, it is recommended to spend moderate time outdoors in the sun, especially during the midday hours when the sun is at its highest point in the sky. However, it’s essential to strike a balance and avoid excessive sun exposure, as prolonged and unprotected exposure to UV radiation can lead to sunburns, premature aging of the skin, and an increased risk of skin cancer. By being mindful of sun safety and making a conscious effort to spend time outdoors, we can leverage the sun’s role in vitamin D production to support our overall health and well-being.
1.2 Benefits of Vitamin D for Your Health
Vitamin D, known as the “sunshine vitamin,” offers a wide range of benefits for our overall health. One of its primary functions is promoting strong bone health by aiding in the absorption of calcium and phosphorus. Sufficient levels of Vitamin D can reduce the risk of conditions such as osteoporosis, rickets, and fractures. Additionally, Vitamin D plays a crucial role in immune function. It helps regulate immune responses, supports the production of antimicrobial peptides, and enhances the function of immune cells. This, in turn, can reduce the risk of infections, including respiratory tract infections. Vitamin D also has the potential to positively impact mental health. Studies suggest that low levels of Vitamin D may be associated with mood disorders such as depression and seasonal affective disorder (SAD). Vitamin D has been linked to a reduced risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. While sunlight is a crucial source of Vitamin D, it’s important to find a balance between sun exposure and protecting our skin from harmful UV radiation. Adequate levels of Vitamin D can also be obtained through dietary sources and supplements, making it a vital nutrient for maintaining optimal health.
1.3 Sunburns and Skin Health
Prolonged exposure to the sun’s harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation can lead to sunburns, which can have detrimental effects on our skin health. Sunburns occur when the skin is exposed to excessive amounts of UV rays, causing inflammation and damage to the skin cells. It’s important to understand that the severity of a sunburn can vary based on factors such as skin type, the intensity of the sun’s rays, and the duration of exposure. Sunburns are not only painful and uncomfortable but can also increase the risk of developing skin cancer later in life.
Protecting our skin from sunburns is paramount to maintaining optimal skin health. One of the most effective ways to prevent sunburns is by applying a broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF (sun protection factor) before going out in the sun. This helps to block both UVA and UVB rays, which are responsible for damaging the skin. Additionally, wearing protective clothing such as wide-brimmed hats, long sleeves, and sunglasses can provide an extra layer of defense against harmful UV radiation.
It’s also important to note that sunburns can affect individuals of all skin tones, and even though certain skin types may have more natural protection against sunburns due to higher amounts of melanin, they are still susceptible to the damaging effects of UV radiation. It’s crucial for everyone to practice sun safety measures and be mindful of sun exposure.
In case of a sunburn, taking immediate action can help alleviate symptoms and promote healing. Applying a cool compress or taking a cool bath can alleviate the discomfort, while moisturizing the skin with soothing lotions or aloe vera gel can help hydrate and nourish the damaged skin. It’s essential to avoid further sun exposure until the sunburn has healed to prevent additional damage.
By being mindful of sun exposure, wearing protective sunscreen, clothing, and practicing overall sun safety, we can protect our skin from sunburns and maintain optimal skin health. Remember, healthy skin is a crucial part of overall well-being and should not be overlooked.
2. Sunlight and Mental Well-being
The influence of sunlight extends beyond physical health and has a significant impact on our mental well-being as well. Sunlight plays a crucial role in the production of serotonin, a neurotransmitter responsible for regulating our mood and feelings of happiness. When we are exposed to sunlight, our bodies produce more serotonin, which can boost our mood and promote a sense of overall well-being. This is why spending time outdoors on sunny days often leaves us feeling happier and more energized. In contrast, a lack of sunlight, particularly during winter months, can lead to a condition known as Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD), which is characterized by feelings of low mood, fatigue, and reduced motivation. It’s important to embrace the healing power of sunlight and find ways to incorporate it into our daily lives to support our mental and emotional health.
2.1 The Influence of Sunlight on Serotonin Levels
Sunlight has a direct influence on our serotonin levels, which is a neurotransmitter responsible for regulating mood and feelings of well-being. When exposed to sunlight, our bodies release serotonin, leading to a boost in mood and overall happiness. This is why many people experience increased feelings of joy and positivity on sunny days. Serotonin also plays a role in regulating appetite, sleep, and cognitive functions. Low levels of serotonin have been associated with conditions like depression, anxiety, and seasonal affective disorder (SAD). Getting enough sunlight can help maintain optimal serotonin levels and support positive mental health. However, it’s important to note that excessive exposure to sunlight can lead to sunburn and other skin damage. So, while enjoying the benefits of sunlight, it’s crucial to find a balance and protect our skin using appropriate sun protection measures. If you’d like to learn more about harnessing energy from different celestial bodies, you might find our article on lunar energy manifestation and intentions interesting.
2.2 Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD)
Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) is a type of depression that affects some individuals during specific seasons, typically during the fall and winter months when there is less sunlight. This condition is thought to be linked to the reduced exposure to natural light. SAD symptoms can include feelings of sadness, lethargy, increased sleepiness, weight gain, and a general lack of motivation.
So, how does the sun play a role in this disorder? Sunlight exposure helps regulate the production of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that affects mood. When there is less sunlight, the production of serotonin may be reduced, leading to the onset of SAD symptoms. Additionally, sunlight exposure can affect the balance of melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep and is associated with depression. Decreased sunlight can disrupt the balance of melatonin, contributing to the development of SAD.
Treatment for SAD often involves light therapy, where individuals sit in front of a special light box that emits bright light mimicking natural sunlight. This therapy helps compensate for the lack of sunlight during the darker months. Other treatments may include psychotherapy, medication, or lifestyle changes, such as increasing physical activity or spending time outdoors during daylight hours.
It’s important to note that not everyone is affected by SAD, and the severity of symptoms can vary from person to person. If you suspect that you or someone you know may be experiencing SAD, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and guidance on treatment options.
3. Sun’s Impact on Sleep Patterns

The sun has a significant impact on our sleep patterns, thanks to its role in regulating our circadian rhythm. Exposure to natural sunlight during the day helps to align our internal body clock with the external environment. This synchronization is crucial for maintaining a healthy sleep-wake cycle. When we are exposed to sunlight, particularly in the morning, it signals to our brain that it’s time to be awake and alert. This exposure also helps to suppress the production of melatonin, a hormone that induces sleepiness. On the other hand, limited exposure to sunlight, especially in the evening or at night, can disrupt our circadian rhythm and make it difficult to fall asleep or wake up at the desired times. It’s important to prioritize regular exposure to natural sunlight, particularly in the morning, as part of a healthy routine to support good sleep.
3.1 Sunlight’s Role in Regulating Circadian Rhythm
Sunlight plays a crucial role in regulating our circadian rhythm, also known as our internal body clock. Our circadian rhythm is responsible for regulating our sleep-wake cycle and other physiological processes that occur over a 24-hour period. Exposure to natural sunlight helps to synchronize our circadian rhythm and keep it in balance. When sunlight enters our eyes, it stimulates the production of a hormone called melatonin, which helps regulate sleep. Sunlight exposure in the morning helps to signal our bodies to wake up and promotes alertness throughout the day. Conversely, exposure to sunlight in the evening can suppress melatonin production, signaling to our bodies that it is time to wind down and prepare for sleep. This natural exposure to sunlight helps ensure that our bodies maintain a healthy sleep-wake cycle. However, it’s important to note that excessive exposure to artificial light, especially in the evening, can disrupt our circadian rhythm and interfere with quality sleep. So, getting a healthy dose of sunlight during the day can help regulate our internal body clock and contribute to a better sleep pattern.
3.2 Importance of a Healthy Sleep-Wake Cycle
A healthy sleep-wake cycle is vital for our overall well-being and daily functioning. When we have a consistent sleep routine, our bodies and minds are better able to regulate various processes, improving our physical and mental health. A healthy sleep-wake cycle allows us to get the recommended hours of sleep each night, which varies depending on age and individual needs. During sleep, our bodies go through important restorative processes, such as muscle repair, memory consolidation, and hormone regulation. Without sufficient sleep, we may experience fatigue, difficulty concentrating, mood swings, and a weakened immune system. Additionally, a disrupted sleep-wake cycle can lead to sleep disorders such as insomnia, sleep apnea, or restless leg syndrome. To maintain a healthy sleep-wake cycle, it is important to establish a consistent bedtime routine, create a sleep-friendly environment, limit exposure to screens before bed, and prioritize relaxation techniques. Prioritizing sleep is essential for optimal health, as it promotes physical and cognitive function, boosts mood, and enhances overall well-being.
4. Balancing Sun Exposure for Good Health
Maintaining a balance between sun exposure and protecting our skin is vital for good health. Here are some guidelines to help you find that balance. Firstly, it’s important to be aware of the optimal sun exposure guidelines. The amount of sun exposure needed varies depending on factors such as skin type, location, and time of day. Generally, experts recommend spending a moderate amount of time in the sun, gradually building up tolerance to avoid sunburns. Secondly, combining sun protection measures with vitamin D production is essential. This can be achieved by wearing protective clothing, using sunscreen with a high SPF, and seeking shade during peak sun hours. Additionally, it’s advisable to supplement with vitamin D, especially for individuals who have limited sun exposure or live in regions with reduced sunlight. By understanding and implementing these strategies, you can enjoy the benefits of the sun while safeguarding your health.
4.1 Optimal Sun Exposure Guidelines
When it comes to sun exposure, it’s important to find a balance that allows us to enjoy the benefits while protecting ourselves from its potential harm. Here are some optimal sun exposure guidelines to keep in mind:
1. Timing: The sun’s rays are strongest between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., so it’s wise to limit direct sun exposure during these hours. If you plan to spend time outdoors, try to schedule activities earlier in the morning or later in the afternoon.
2. Duration: The ideal amount of sun exposure varies depending on factors such as your skin type and geographical location. Generally, it is recommended to spend about 10 to 30 minutes in the sun, without sunscreen, a few times a week. This allows your body to produce an adequate amount of Vitamin D.
3. Protection: When spending prolonged periods in the sun, it’s essential to protect your skin. Wear loose-fitting clothing that covers your body, a wide-brimmed hat to shield your face, and sunglasses to protect your eyes. Apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher, and reapply every two hours or after swimming or sweating.
4. Seek shade: If the sun’s rays become too intense or you start to feel overheated, find shade to cool down and give your skin a break from direct exposure.
Remember, these guidelines are meant to help you make informed decisions about sun exposure, but individual needs may vary. Consulting with a healthcare professional or dermatologist can provide personalized advice based on your specific circumstances.
4.2 Combining Sun Protection and Vitamin D Production
Combining sun protection and vitamin D production is essential for maintaining optimal health. While it’s crucial to protect our skin from the harmful effects of UV radiation, it’s also important to ensure that our bodies receive an adequate amount of vitamin D. Luckily, there are several strategies we can use to strike this balance. One option is to plan our sun exposure during the early morning or late afternoon hours when the sun’s rays are less intense. This allows us to enjoy the benefits of natural sunlight while reducing the risk of sunburn. Additionally, wearing protective clothing such as long sleeves, hats, and sunglasses can shield our skin from direct exposure to the sun. Sunscreen should also be a part of our sun protection routine, with a broad-spectrum sunscreen (which protects against both UVA and UVB rays) of at least SPF 30 applied generously to all exposed skin. However, it’s important to note that sunscreen can inhibit the body’s ability to produce vitamin D, as it blocks the UV rays necessary for synthesis. It’s recommended to spend some time in the sun without sunscreen, aiming for around 10-15 minutes, depending on the skin’s sensitivity and the intensity of the sun’s rays. This allows the body to produce vitamin D while still taking precautions to prevent sunburn. It’s also worth considering vitamin D supplements, especially if sun exposure is limited or if certain factors (such as living in higher latitudes) make it difficult to obtain sufficient vitamin D naturally. By combining sun protection measures with mindful sun exposure, we can maintain healthy levels of vitamin D while minimizing the risks associated with excessive sun exposure.
Conclusion

In conclusion, the sun plays a crucial role in our overall well-being, impacting both our physical and mental health. By understanding the effects of sun exposure, we can harness its benefits while taking necessary precautions to protect ourselves. Vitamin D production, influenced by sunlight, is essential for various bodily functions, including bone health and immune system support. However, it’s important to be mindful of sunburns and the potential risks they pose to our skin health. Sunlight also influences our mental well-being, with serotonin levels affected by exposure to natural light. Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) is a condition that highlights the significance of sunlight in maintaining positive mental health. Additionally, the sun’s influence on our sleep patterns through regulating our circadian rhythm emphasizes the importance of a healthy sleep-wake cycle. By following optimal sun exposure guidelines, we can strike a balance between benefiting from the sun and protecting ourselves from harmful effects. This includes using sun protection methods like sunscreen, protective clothing, and seeking shade during peak hours. Remember that good health is a holistic endeavor, and the sun is an essential component in achieving overall well-being. So, go out, enjoy the sun responsibly, and let it contribute to a healthier and happier you.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can I get enough Vitamin D from the sun alone?
Yes, spending time outdoors and exposing your skin to sunlight can help your body produce Vitamin D naturally. However, depending on factors such as your location, time of year, and skin pigmentation, you may need to supplement with Vitamin D-rich foods or supplements to meet your daily requirements.
2. How much sun exposure is considered safe?
The amount of sun exposure considered safe varies depending on various factors such as your skin type, location, and time of day. Generally, experts recommend getting moderate sun exposure for about 10-30 minutes, two to three times a week, without sunscreen, to allow your body to produce Vitamin D.
3. Can too much sun exposure be harmful?
Yes, excessive sun exposure can be harmful to your skin. It can lead to sunburns, premature aging, and an increased risk of developing skin cancer. It is crucial to protect your skin by wearing sunscreen, seeking shade during peak sun hours, and wearing protective clothing when spending extended periods outdoors.
4. Does sunscreen prevent Vitamin D production?
Sunscreen with a high SPF can reduce the production of Vitamin D in the skin. However, it is recommended to apply sunscreen after getting a few minutes of sun exposure to ensure your skin is protected from harmful UV rays while still allowing some Vitamin D synthesis to occur.
5. Can the sun help improve my mood?
Yes, sunlight has been linked to an improved mood and increased levels of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that plays a role in regulating mood. Spending time outdoors, particularly during daylight hours, can have a positive effect on your mental well-being.
6. What is Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD)?
SAD is a type of depression that usually occurs during the fall and winter months when there is less sunlight. It is believed to be linked to reduced exposure to natural light and can cause symptoms such as low energy, mood swings, and a decrease in overall well-being.
7. How does sunlight affect my sleep patterns?
Sunlight helps regulate our internal body clock, also known as the circadian rhythm. Adequate exposure to natural light during the day can promote better sleep at night, while limited exposure to light in the evening can signal our bodies to prepare for restful sleep.
8. Can lack of sun exposure cause vitamin deficiencies?
Yes, a lack of sun exposure can lead to Vitamin D deficiency. This is especially common in regions with limited sunlight or during the winter months. If you are unable to get enough sun exposure, it is recommended to consult your doctor about supplementing with Vitamin D.
9. Can I get too much Vitamin D from the sun?
While it is rare, it is possible to get too much Vitamin D from excessive sun exposure. However, the body has a natural mechanism that limits the amount of Vitamin D it produces, so it is more likely to occur from consuming excessively high doses of Vitamin D supplements.
10. Can sun exposure affect my immune system?
Yes, moderate sun exposure has been linked to a strengthened immune system. Vitamin D, produced through sun exposure, plays a key role in supporting immune function and helps protect against certain diseases. However, it’s important to strike a balance and protect your skin from excessive sun exposure to minimize the risk of skin damage.
References
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can the sun exposure improve my mood?
Absolutely! Sun exposure stimulates the production of serotonin, a hormone that boosts mood and promotes feelings of happiness.
2. Why is vitamin D important for my health?
Vitamin D plays a crucial role in bone health, immune function, and the prevention of chronic diseases such as cancer and heart disease.
3. How can sunlight affect my sleep patterns?
Sunlight helps regulate your circadian rhythm, which is responsible for your sleep-wake cycle. Exposure to natural light during the day can improve sleep quality at night.
4. Is it true that sunburns contribute to skin aging?
Yes, sunburns can damage the DNA in your skin cells, leading to premature aging, wrinkles, and an increased risk of skin cancer.
5. What are the optimal guidelines for sun exposure?
Experts recommend getting around 10-30 minutes of unprotected sun exposure between 10 am and 3 pm, depending on your skin type and location.
6. Can I get enough vitamin D through sunlight alone?
In most cases, it is challenging to get enough vitamin D through sunlight alone. Supplementation or consuming vitamin D-rich foods may be necessary.
7. Can lack of sunlight cause seasonal affective disorder (SAD)?
Yes, lack of sunlight during the winter months can disrupt your body’s natural rhythm and lead to symptoms of seasonal affective disorder, such as depression and fatigue.
8. How can I protect my skin from the harmful effects of the sun?
Wearing sunscreen with a high SPF, protective clothing, and seeking shade during peak sun hours can help prevent sunburns and reduce the risk of skin damage.
9. Is it possible to get too much sun exposure?
Yes, excessive sun exposure can increase the risk of skin cancer, premature aging, and sunburns. It’s important to find a balance and take proper precautions.
10. Can the sun improve my overall well-being?
Yes, the sun’s benefits extend beyond physical health. Sunlight can improve mood, promote better sleep, and enhance overall well-being by providing a sense of vitality and connection to the natural world.






